The total population of the Philippines back in 2020 totalled approximately 110 million people. That year, there were an estimated 591,000 people who developed TB. Among them, 73,000 were children. Moreover, there were 334,459 missing people with TB, of which 54,551 were children.
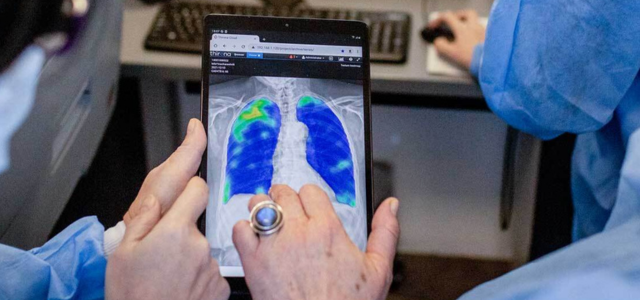
In 2018, Delft Imaging collaborated with FIND and the International Organization for Migration (IOM) on using the CAD4TB artificial intelligence software to detect TB-related abnormalities on chest X-rays automatically.
Later, in 2021, we delivered CAD4TB to eight sites as part of the large iNTP project, funded by USAID and supported by the Stop TB Partnership. The project came with installation, training and long-term maintenance services.
In 2022, Delft Imaging delivered additional CAD4TB software to the Philippines to be used by Medecins Sans Frontieres (MSF). The project again featured installation, training and long-term maintenance services.
Making a difference
In a study published and presented during the Union World Conference on Lung Health in 2015, CAD4TB was utilised in the Palawan provincial areas of the Philippines. The study then used CAD4TB 4 (an older version of CAD4TB than what is currently available), and the software achieved a sensitivity of 90% and a specificity of 80%. The study concluded that computerised reading (artificial intelligence) provides high sensitivity and specificity and may assist human readers in active case-finding programs, thus improving screening throughput.
In a study published in 2019, researchers looked at automated chest X-ray readings for tuberculosis in the Philippines to improve case detection. The study examined 10,755 individuals, of which 2,534 had a positively assessed chest X-ray and 298 Xpert-positive cases. The publication noted that based on the radiological reference, the physician performed slightly worse than the CAD4TB software, although it was not found to be statistically significant at that time. The study concluded that the performance of automated chest X-ray reading is comparable to that of attending physicians, and its use as a second reader could increase TB case detection. Note that the study used an older version of CAD4TB than currently available.
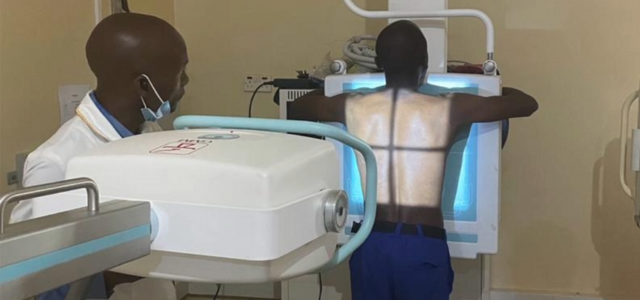
The 2023 USAID report highlights the use of CAD4TB software, an AI-powered tool, integrated with ultra-portable digital X-ray systems to boosts TB screening in remote areas of Philippines. CAD4TB’s application significantly improved the efficiency of diagnosing TB by rapidly analyzing chest X-rays to detect abnormalities that may indicate the presence of TB. This technology, coupled with the ultra-portable nature of the X-ray equipment, facilitated quick and accurate TB screenings, reducing the typical result turnaround time from three days to a mere 2-3 minutes. This capability proved crucial in increasing access to TB diagnostic services for geographically isolated and disadvantaged communities, streamlining the detection process and enabling prompt initiation of preventive treatment where necessary.
Case Study
In the Philippines, to address the high number of undiagnosed TB cases, ultra-portable X-ray systems with CAD4TB software were deployed, significantly increasing TB screenings and detections in challenging and underserved areas. Learn how this initiative is transforming TB diagnosis and treatment in the country through the case study “Active TB Case-finding among High-risk Groups.”
A TB screening initiative using digital CXR and CAD4TB identified a high TB rate, underscoring the tool’s effectiveness in detecting cases, particularly among asymptomatic individuals. This approach highlights the importance of active case-finding and addressing the challenges in treatment initiation. Learn more about the impact of this innovative screening strategy through the case study “Active TB Case-finding with CAD4TB.”